How Long Does It Take To Get Oil Changed
How long does information technology have to get to Mars?

If you wanted to travel to Mars, how long would it accept? The answer depends on several factors, ranging from the position of the planets to the technology that would propel you lot there.
According to NASA, a ane-mode trip to Mars would accept about 9 months. If you wanted to brand it a circular-trip, all in all, it would take nearly 21 months every bit you lot will demand to wait nigh three months on Mars to make sure Earth and Mars are in a suitable location to brand the trip back home.
Nosotros take a look at how long a trip to the Ruby-red Planet would take using available technology and explore some of the factors that would affect your travel fourth dimension.
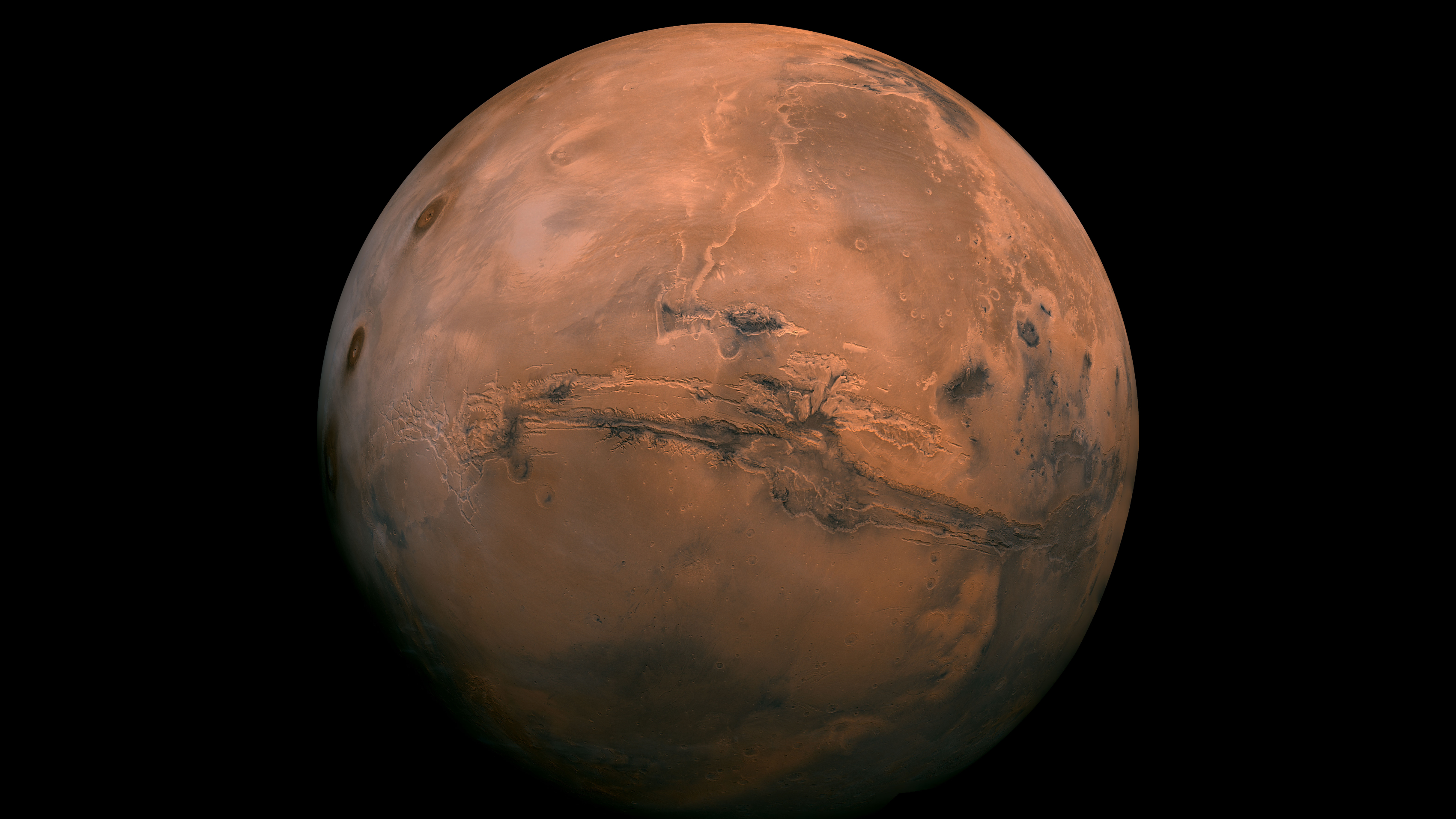
How far away is Mars?
To determine how long it will have to achieve Mars, nosotros must starting time know the distance betwixt the 2 planets.
Mars is the fourth planet from the dominicus, and the second closest to Earth (Venus is the closest). But the altitude between Earth and Mars is constantly changing every bit they travel effectually the sun.
In theory, the closest that Earth and Mars would approach each other would be when Mars is at its closest bespeak to the sun (perihelion) and World is at its farthest (aphelion). This would put the planets only 33.9 million miles (54.half-dozen million kilometers) apart. However, this has never happened in recorded history. The closest recorded approach of the two planets occurred in 2003 when they were only 34.8 1000000 miles (56 million km) autonomously.
The two planets are farthest apart when they are both at their farthest from the lord's day, on reverse sides of the star. At this point, they can be 250 million miles (401 million km) apart.
The average distance between Earth and Mars is 140 million miles (225 meg km).
Related: What is the temperature on Mars?
How long would it take to travel to Mars at the speed of light?
Light travels at approximately 186,282 miles per second (299,792 km per 2d). Therefore, a low-cal shining from the surface of Mars would take the following corporeality of time to reach Earth (or vice versa):
- Closest possible arroyo: 182 seconds, or 3.03 minutes
- Closest recorded approach: 187 seconds, or 3.eleven minutes
- Farthest arroyo: 1,342 seconds, or 22.4 minutes
- On average: 751 seconds, or merely over 12.5 minutes
Fastest spacecraft so far
The fastest spacecraft is NASA's Parker Solar Probe, as information technology keeps breaking its own speed records as it moves closer to the sun. On Nov 21, 2021 the Parker Solar Probe reached a top speed of 101 miles (163 kilometers) per 2nd during its 10th close flyby of our star, which translates to an eye-watering 364,621 mph (586,000 kph). Co-ordinate to a NASA statement, when the Parker Solar Probe comes within iv meg miles (half dozen.2 million kilometers) of the solar surface in December 2024, the spacecraft's speed volition pinnacle 430,000 miles per 60 minutes!
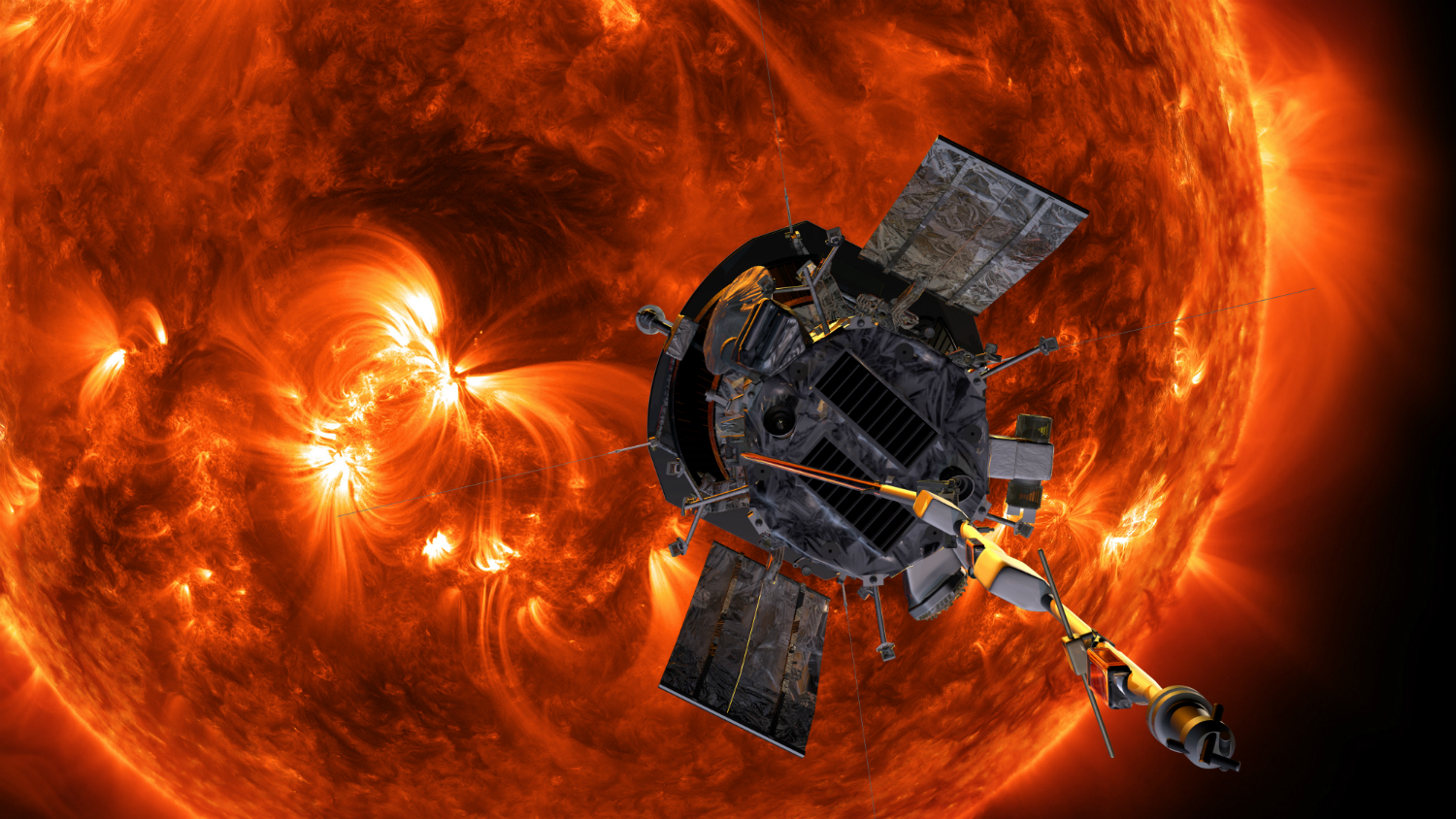

If the Parker Solar Probe managed to attain the speeds reached during its 10th close flyby of the Sun and took a detour from its sun-focused mission to travel in a straight line from Earth to the Ruby Planet, the fourth dimension it would take to get to Mars would exist:
- Closest possible approach: 93 hours
- Closest recorded approach: 95 hours
- Farthest approach: 686 hours (28.5 days)
- On boilerplate: 384 hours (16 days)
The problems with calculating travel times to Mars
Of form, the problem with the previous calculations is that they measure the distance between the ii planets equally a directly line. Traveling through the farthest passing of Earth and Mars would involve a trip directly through the dominicus, while spacecraft must of necessity move in orbit around the solar system'southward star.
Although this isn't a trouble for the closest approach, when the planets are on the aforementioned side of the sun, some other trouble exists. The numbers also assume that the two planets remain at a constant altitude; that is, when a probe is launched from Earth while the two planets are at the closest approach, Mars would remain the same distance abroad over the 39 days it took the probe to travel.
Related: A brief history of Mars missions
In reality, however, the planets are continuously moving in their orbits effectually the sunday. Engineers must summate the ideal orbits for sending a spacecraft from Earth to Mars. Their numbers factor in not only distance but also fuel efficiency. Like throwing a dart at a moving target, they must calculate where the planet will exist when the spacecraft arrives, non where it is when it leaves Earth. Spaceships must too decelerate to enter orbit effectually a new planet to avoid overshooting it.
How long it takes to attain Mars depends on where in their orbits the two planets lie when a mission is launched. Information technology too depends on the technological developments of propulsion systems.
According to NASA Goddard Space Flight Center's website, the ideal lineup for a launch to Mars would become you to the planet in roughly 9 months. The website quotes physics professor Craig C. Patten, of the Academy of California, San Diego:
"It takes the Earth one year to orbit the lord's day and information technology takes Mars about 1.9 years (say 2 years for like shooting fish in a barrel calculation) to orbit the sun. The elliptical orbit which carries you from Earth to Mars is longer than Globe's orbit but shorter than Mars' orbit. Accordingly, we can gauge the fourth dimension it would take to complete this orbit by averaging the lengths of World's orbit and Mars' orbit. Therefore, it would take about 1 and a one-half years to complete the elliptical orbit.
"In the 9 months information technology takes to get to Mars, Mars moves a considerable distance around in its orbit, about three-eighths of the way around the sun. You lot have to plan to make sure that by the fourth dimension y'all reach the distance of Mar's orbit, Mars is where you demand it to be! Practically, this means that you can but begin your trip when Earth and Mars are properly lined upward. This only happens every 26 months. That is, there is merely one launch window every 26 months."
The trip could be shortened past called-for more fuel — a process non ideal with today's technology, Patten said.
Evolving technology can help to shorten the flight. NASA's Space Launch System (SLS) will exist the new workhorse for carrying upcoming missions, and potentially humans, to the red planet. SLS is currently being constructed and tested, with NASA now targeting a launch in March or April 2022 for its Artemis one flight, the starting time flight of its SLS rocket.
Robotic spacecraft could i twenty-four hour period make the trip in simply three days. Photon propulsion would rely on a powerful light amplification by stimulated emission of radiation to accelerate spacecraft to velocities budgeted the speed of light. Philip Lubin, a physics professor at the Academy of California, Santa Barbara, and his squad are working on the Directed Energy Propulsion for Interstellar Exploration (DEEP-IN). The method could propel a 220-lb. (100 kilograms) robotic spacecraft to Mars in only iii days, he said.
"There are recent advances which accept this from scientific discipline fiction to science reality," Lubin said at the 2015 NASA Innovative Advanced Concepts (NIAC) autumn symposium. "In that location's no known reason why we cannot do this."
How long did past missions take to reach Mars?
Here is an infographic detailing how long it took several historical missions to reach the Crimson Planet (either orbiting or landing on the surface). Their launch dates are included for perspective.

Additional resources
Explore NASA's lunar exploration plans with their Moon to Mars overview. You tin can read most how to get people from World to Mars and safely back again with this informative article on The Conversation. Curious about the homo health risks of a mission to the Cerise Planet? You may find this enquiry paper of particular interest.
Bibliography
- Lubin, Philip. "A roadmap to interstellar flight." arXiv preprint arXiv:1604.01356 (2016).
- Donahue, Ben B. "Futurity Missions for the NASA Infinite Launch System." AIAA Propulsion and Energy 2021 Forum. 2021.
- Srinivas, Susheela. "Hop, Skip and Jump—The Moon to Mars Mission." (2019).
Join our Infinite Forums to keep talking space on the latest missions, dark sky and more! And if you take a news tip, correction or annotate, let us know at: community@space.com.
Source: https://www.space.com/24701-how-long-does-it-take-to-get-to-mars.html
Posted by: lockettliblaingledy.blogspot.com


0 Response to "How Long Does It Take To Get Oil Changed"
Post a Comment